Here are the essential concepts you must grasp in order to answer the question correctly.
Newton's Law of Universal Gravitation
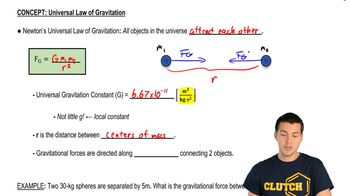
Newton's Law of Universal Gravitation states that every mass attracts every other mass in the universe with a force that is directly proportional to the product of their masses and inversely proportional to the square of the distance between their centers. This principle is essential for understanding how objects, such as clumps of matter orbiting a black hole, are influenced by gravitational forces.
Recommended video:
Universal Law of Gravitation
Centripetal Force
Centripetal force is the net force required to keep an object moving in a circular path, directed towards the center of the circle. In the context of the black hole, the gravitational force exerted by the black hole provides the necessary centripetal force to keep the orbiting matter in its circular path, allowing us to relate the orbital speed and radius to the mass of the black hole.
Recommended video:
Intro to Centripetal Forces
Mass of the Sun
The mass of the Sun is a standard reference point in astrophysics, approximately 1.989 x 10^30 kilograms. When calculating the mass of astronomical objects like black holes, it is common to express their mass as a multiple of the Sun's mass, facilitating easier comparisons and understanding of their scale relative to our solar system.
Recommended video: