Here are the essential concepts you must grasp in order to answer the question correctly.
Work-Energy Theorem
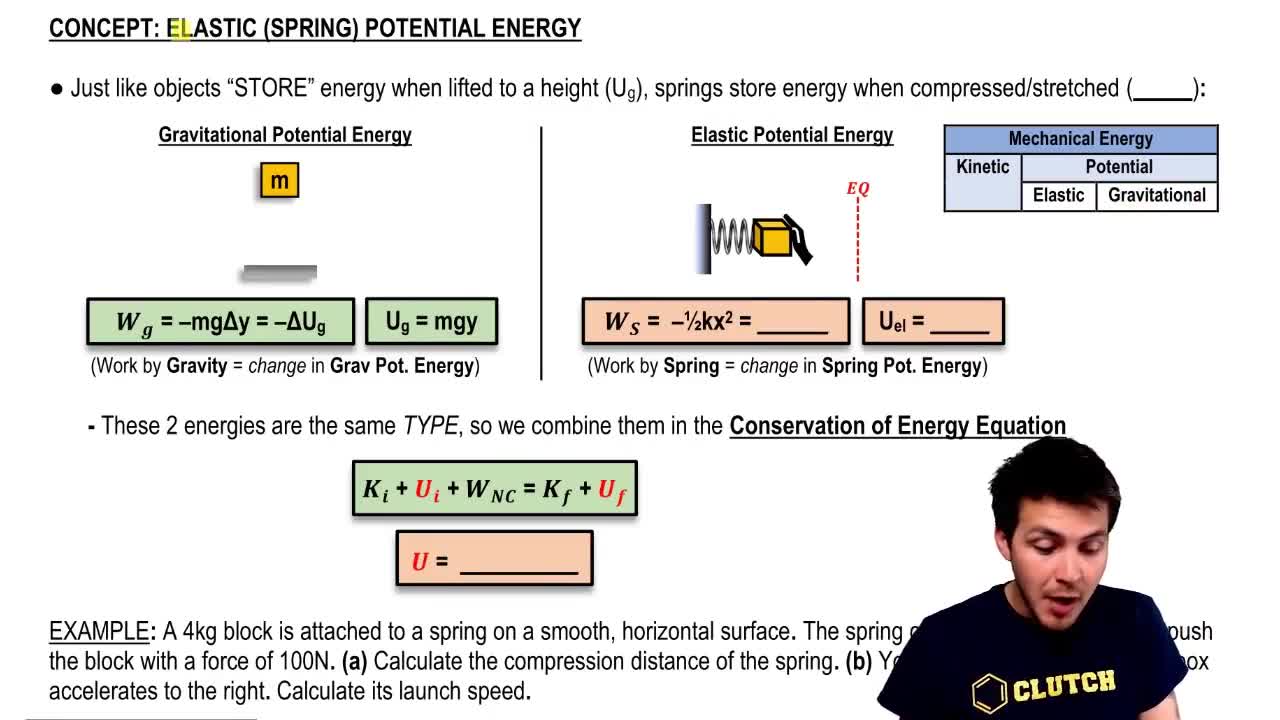
The work-energy theorem states that the work done on an object is equal to the change in its kinetic energy. In this scenario, the kinetic energy of the box will be converted into the potential energy stored in the spring as it compresses. This principle allows us to relate the initial kinetic energy of the box to the maximum potential energy of the spring at maximum compression.
Recommended video:
Kinetic Energy
Kinetic energy is the energy an object possesses due to its motion, calculated using the formula KE = 1/2 mv², where m is the mass and v is the velocity. For the box in this problem, its initial kinetic energy can be determined using its mass (6.0 kg) and its velocity (3.0 m/s). This energy will be transferred to the spring as it compresses.
Recommended video:
Intro to Rotational Kinetic Energy
Spring Potential Energy
Spring potential energy is the energy stored in a compressed or stretched spring, given by the formula PE = 1/2 kx², where k is the spring constant and x is the compression or extension from its equilibrium position. In this case, the spring constant is given as 75 N/cm, which must be converted to N/m for calculations. The maximum compression of the spring can be found by equating the initial kinetic energy of the box to the potential energy of the spring.
Recommended video:
Energy in Horizontal Springs