A small car of mass kg is pushing a large truck of mass kg due east on a level road. The car exerts a horizontal force of N on the truck. What is the magnitude of the force that the truck exerts on the car?

Crates and sit at rest side by side on a frictionless horizontal surface. They have masses and , respectively. When a horizontal force is applied to crate , the two crates move off to the right. Draw clearly labeled free-body diagrams for crate and for crate . Indicate which pairs of forces, if any, are third-law action–reaction pairs.
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance
Verified video answer for a similar problem:
Key Concepts
Free-Body Diagram

Newton's Third Law of Motion
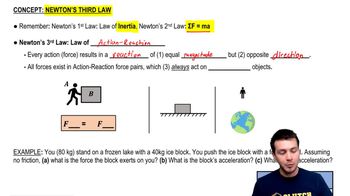
Frictionless Surface

World-class sprinters can accelerate out of the starting blocks with an acceleration that is nearly horizontal and has magnitude m/s2. How much horizontal force must a -kg sprinter exert on the starting blocks to produce this acceleration? Which body exerts the force that propels the sprinter: the blocks or the sprinter herself?
Boxes and are in contact on a horizontal, frictionless surface (Fig. E). Box has mass kg and box has mass kg. A horizontal force of N is exerted on box . What is the magnitude of the force that box exerts on box ?
A ball is hanging from a long string that is tied to the ceiling of a train car traveling eastward on horizontal tracks. An observer inside the train car sees the ball hang motionless. Draw a clearly labeled free-body diagram for the ball if the train is speeding up uniformly. Is the net force on the ball zero in either case? Explain.
