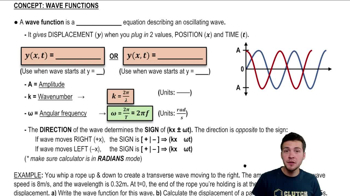
Here are the essential concepts you must grasp in order to answer the question correctly.
Vector Representation
Vectors are quantities that have both magnitude and direction, represented in a coordinate system. In this case, vectors A and B are expressed in terms of their components along the x-axis (i) and y-axis (j). Understanding how to interpret these components is essential for calculating angles and performing vector operations.
Recommended video:
Adding 3 Vectors in Unit Vector Notation
Angle with the x-axis
The angle a vector makes with the positive x-axis can be determined using the arctangent function. Specifically, for a vector A with components (Ax, Ay), the angle θ is given by θ = arctan(Ay/Ax). This angle is measured counterclockwise from the positive x-axis, which is crucial for determining the orientation of the vector in the Cartesian plane.
Recommended video:
Trigonometric Functions
Trigonometric functions, particularly sine, cosine, and tangent, are fundamental in relating angles to the ratios of the sides of right triangles. In the context of vectors, these functions help in calculating angles and understanding the geometric relationships between vectors and their components. They are essential for solving problems involving angles and directions in physics.
Recommended video:
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance