Here are the essential concepts you must grasp in order to answer the question correctly.
X-ray Production
X-rays are produced when high-energy electrons collide with a metal target, resulting in the emission of electromagnetic radiation. The energy of the emitted X-rays is directly related to the kinetic energy of the electrons, which is determined by the acceleration voltage applied in the cathode-ray tube.
Recommended video:
Introduction to Dot Product (Scalar Product)
Wavelength and Energy Relationship
The energy of a photon is inversely related to its wavelength, described by the equation E = hc/λ, where E is energy, h is Planck's constant, c is the speed of light, and λ is the wavelength. This relationship indicates that higher energy photons correspond to shorter wavelengths, which is crucial for calculating the shortest-wavelength X-rays produced.
Recommended video:
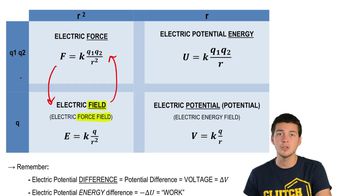
Relationships Between Force, Field, Energy, Potential
Acceleration Voltage
The acceleration voltage in a cathode-ray tube determines the maximum kinetic energy of the electrons. In this case, a voltage of 15.0 kV means that the electrons can gain up to 15,000 electron volts of energy, which can then be converted into X-ray photons upon impact with the target, influencing the wavelength of the emitted X-rays.
Recommended video:
 Young & Freedman Calc 14th Edition
Young & Freedman Calc 14th Edition Ch 01: Units, Physical Quantities & Vectors
Ch 01: Units, Physical Quantities & Vectors Problem 38
Problem 38 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance