Here are the essential concepts you must grasp in order to answer the question correctly.
Capacitance
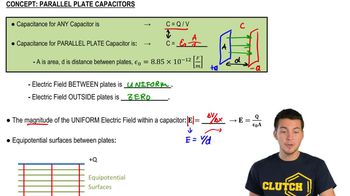
Capacitance is the ability of a system to store electric charge per unit voltage. It is defined as the ratio of the electric charge (Q) stored on the electrodes to the potential difference (V) across them, expressed as C = Q/V. The unit of capacitance is the farad (F), and it is influenced by the physical characteristics of the capacitor, including the area of the electrodes and the distance between them.
Recommended video:
Capacitors & Capacitance (Intro)
Parallel Plate Capacitor
A parallel plate capacitor consists of two conductive plates separated by an insulating material (dielectric). The capacitance of such a capacitor can be calculated using the formula C = ε₀(A/d), where ε₀ is the permittivity of free space, A is the area of one of the plates, and d is the separation between the plates. This model simplifies the analysis of capacitors and is fundamental in understanding how they operate.
Recommended video:
Parallel Plate Capacitors
Electric Field
The electric field (E) is a vector field that represents the force per unit charge experienced by a positive test charge placed in the field. For a parallel plate capacitor, the electric field is uniform between the plates and can be calculated using E = V/d, where V is the voltage across the plates and d is the separation distance. Understanding the electric field is crucial for analyzing how capacitors store energy and influence charge distribution.
Recommended video: