Here are the essential concepts you must grasp in order to answer the question correctly.
Heat of Combustion
The heat of combustion is the amount of energy released when a substance is burned completely in oxygen. For coal, this value is approximately 28 MJ/kg, meaning that burning one kilogram of coal produces 28 megajoules of energy. This concept is crucial for calculating the total energy produced from a given mass of coal, which directly relates to the power output of the plant.
Recommended video:
Overview of Heat Transfer
Power and Energy Relationship
Power is the rate at which energy is produced or consumed, measured in watts (W), where 1 watt equals 1 joule per second. In this context, the power plant generates 750 MW, which means it produces 750 million joules of energy every second. Understanding this relationship allows us to determine how much energy is needed to operate the plant over a specified time, such as one day.
Recommended video:
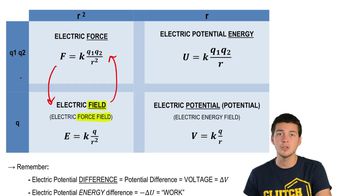
Relationships Between Force, Field, Energy, Potential
Volume and Density
Density is defined as mass per unit volume, typically expressed in kg/m³. For coal, the density is 1500 kg/m³, which means that one cubic meter of coal weighs 1500 kilograms. This concept is essential for calculating the volume of coal needed to sustain the power plant's operation for a day, as it allows us to convert the total mass of coal required into a physical volume.
Recommended video:
Problems with Mass, Volume, & Density