Here are the essential concepts you must grasp in order to answer the question correctly.
Thermodynamic Processes
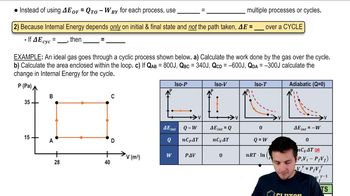
Thermodynamic processes describe the changes in state of a system, such as a gas, as it exchanges energy with its surroundings. These processes can be classified into isothermal, adiabatic, isobaric, and isochoric, each characterized by specific conditions regarding temperature, pressure, and volume. Understanding these processes is crucial for analyzing how heat energy is transferred during each segment of the process.
Recommended video:
Properties of Cyclic Thermodynamic Processes
Heat Transfer
Heat transfer refers to the movement of thermal energy from one object or system to another due to a temperature difference. It can occur through conduction, convection, or radiation. In the context of the question, calculating the heat energy transferred during each segment involves applying the principles of heat transfer to determine how much energy is gained or lost by the helium gas.
Recommended video:
Overview of Heat Transfer
First Law of Thermodynamics
The First Law of Thermodynamics, also known as the law of energy conservation, states that the total energy of an isolated system remains constant. It can be expressed as ΔU = Q - W, where ΔU is the change in internal energy, Q is the heat added to the system, and W is the work done by the system. This principle is essential for calculating the heat energy transferred in each segment of the thermodynamic process involving the helium gas.
Recommended video:
The First Law of Thermodynamics
 Knight Calc 5th Edition
Knight Calc 5th Edition Ch 19: Work, Heat, and the First Law of Thermodynamics
Ch 19: Work, Heat, and the First Law of Thermodynamics Problem 19
Problem 19 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance