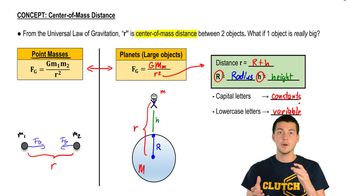
Here are the essential concepts you must grasp in order to answer the question correctly.
Gravitational Potential Energy
Gravitational potential energy (U) in a two-body system is the energy associated with the gravitational interaction between the two masses. It is given by the formula U = -G(m1*m2)/r, where G is the gravitational constant, m1 and m2 are the masses of the two objects, and r is the distance between their centers. A negative value indicates that the gravitational force is attractive, and the energy decreases as the objects come closer.
Recommended video:
Gravitational Potential Energy
Mass and Distance Relationship
In gravitational interactions, the force and potential energy depend on the masses of the objects and the distance between them. For two stars, if one star has a mass M, and the other has a mass 2M, the gravitational potential energy will reflect this relationship. Understanding how mass influences gravitational potential energy is crucial for solving problems involving multiple bodies in space.
Recommended video:
Units of Measurement in Astronomy
In astronomy, distances are often measured in light years (ly), which is the distance light travels in one year, approximately 9.46 trillion kilometers. This unit is essential for understanding the vast distances between celestial objects. Additionally, energy is measured in joules (J), and knowing how to convert and relate these units is important for calculations involving gravitational potential energy and mass.
Recommended video:
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance