Here are the essential concepts you must grasp in order to answer the question correctly.
Conservation of Momentum
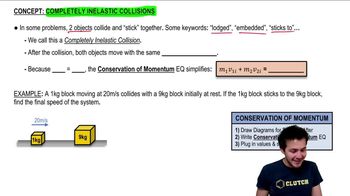
The principle of conservation of momentum states that the total momentum of a closed system remains constant if no external forces act on it. In collisions, the momentum before the collision equals the momentum after the collision. This concept is crucial for solving problems involving collisions, as it allows us to calculate the final velocities of the objects involved.
Recommended video:
Vector Addition
In physics, velocity is a vector quantity, meaning it has both magnitude and direction. To find the resultant velocity of the entangled vehicles after the collision, we must use vector addition to combine their individual momenta. This involves breaking down the velocities into their components and summing them accordingly to determine the overall speed and direction.
Recommended video:
Vector Addition By Components
Inelastic Collision
An inelastic collision is a type of collision where the colliding objects stick together after impact, resulting in a loss of kinetic energy. In this scenario, the truck and the two cars become entangled and move as a single body post-collision. Understanding inelastic collisions is essential for analyzing the final state of the system and calculating the combined mass and velocity.
Recommended video:
Completely Inelastic Collilsions