Here are the essential concepts you must grasp in order to answer the question correctly.
Conservation of Momentum
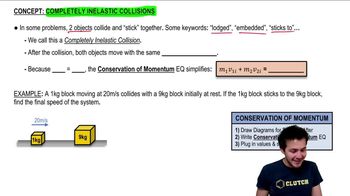
The conservation of momentum states that in a closed system, the total momentum before an event must equal the total momentum after the event, provided no external forces act on it. In this scenario, the car and the clay form a closed system where the momentum of the car before the collision must equal the combined momentum of the car and clay after they stick together.
Recommended video:
Momentum Calculation
Momentum is calculated as the product of an object's mass and its velocity (p = mv). For the car, its momentum can be calculated using its mass (1500 kg) and its velocity (2.0 m/s). The clay's momentum will depend on its mass and the velocity at which it is fired, which we need to determine to achieve the desired outcome of stopping the car.
Recommended video:
Inelastic Collision
An inelastic collision occurs when two objects collide and stick together, resulting in a loss of kinetic energy but conservation of momentum. In this problem, the clay will collide with the car and stick to it, making it an inelastic collision. This concept is crucial for understanding how the velocities of the car and clay will change after the collision.
Recommended video:
Completely Inelastic Collilsions