Here are the essential concepts you must grasp in order to answer the question correctly.
Potential Energy
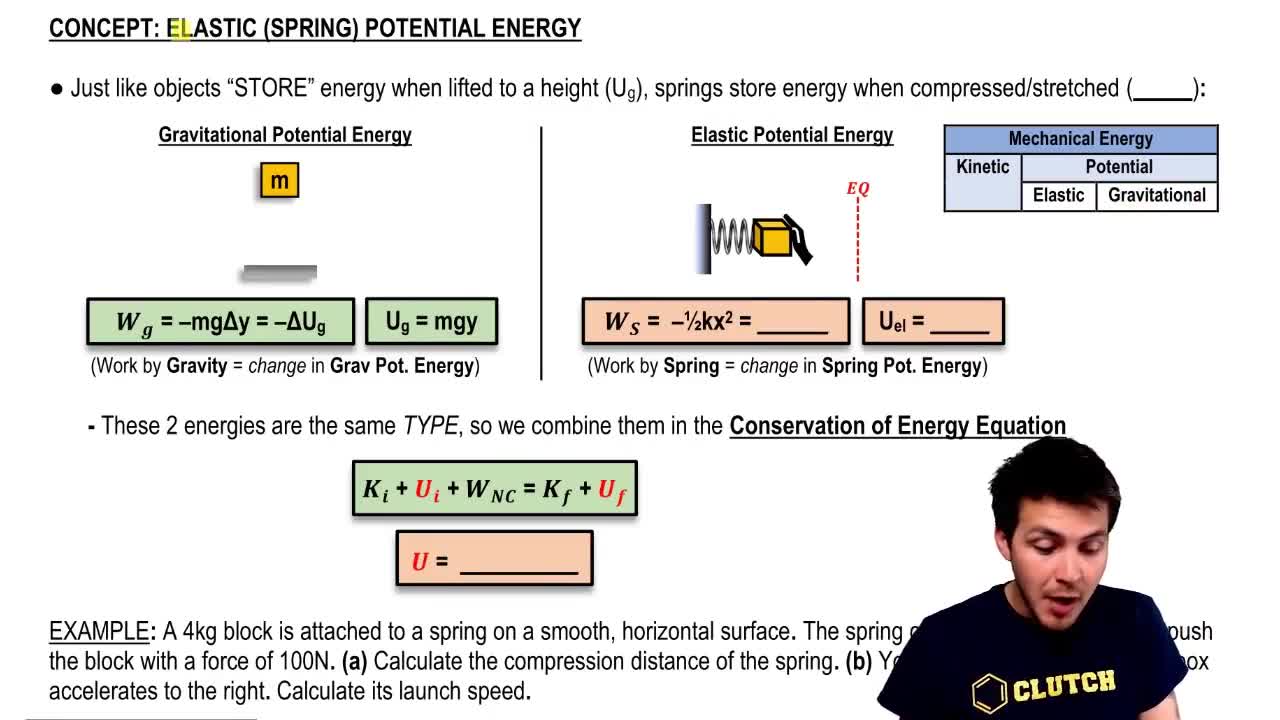
Potential energy is the energy stored in an object due to its position in a gravitational field. In the context of the roller coaster, as the car ascends the 10-meter hill, it gains gravitational potential energy, which can be calculated using the formula PE = mgh, where m is mass, g is the acceleration due to gravity, and h is the height. This energy is crucial for understanding how the car will move as it descends.
Recommended video:
Spring Potential Energy
Spring potential energy is the energy stored in a compressed or stretched spring, described by Hooke's Law. The formula for spring potential energy is PE_spring = 1/2 k x^2, where k is the spring constant and x is the compression or extension of the spring. This concept is essential for determining how much energy the spring can provide to the roller coaster car when fully compressed.
Recommended video:
Energy in Horizontal Springs
Conservation of Energy
The principle of conservation of energy states that energy cannot be created or destroyed, only transformed from one form to another. In this scenario, the total mechanical energy of the roller coaster car will be conserved as it moves from the spring's potential energy to kinetic energy and gravitational potential energy. Understanding this principle allows us to calculate the maximum speed of the car at the lowest point of the track.
Recommended video:
Conservation Of Mechanical Energy