Here are the essential concepts you must grasp in order to answer the question correctly.
Potential Energy (U)
Potential energy is the energy stored in a system due to the position of an object within a force field, such as gravitational or elastic fields. In this context, the potential energy graph shows how the energy varies with the position of the particle. The height of the graph at any point indicates the potential energy of the particle at that position.
Recommended video:
Gravitational Potential Energy
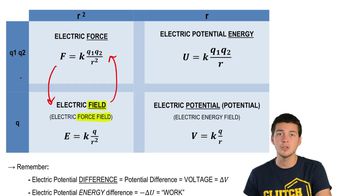
Force and Potential Energy Relationship
The force acting on a particle can be derived from the potential energy function using the relationship F = -dU/dx, where F is the force, U is the potential energy, and x is the position. This means that the force is equal to the negative slope of the potential energy graph at a given position, indicating how the potential energy changes with position.
Recommended video:
Relationships Between Force, Field, Energy, Potential
Calculating the x-component of Force
To find the x-component of the force at specific positions (5, 15, and 25 cm), one must evaluate the slope of the potential energy graph at those points. For positions where the potential energy is constant (like between 4 cm and 8 cm), the force will be zero, while at points where the slope is negative or positive, the force will have corresponding negative or positive values.
Recommended video:
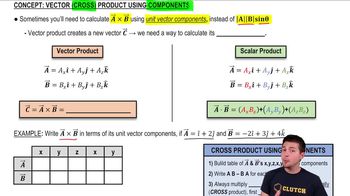
Calculating the Vector (Cross) Product Using Components