Here are the essential concepts you must grasp in order to answer the question correctly.
Conservation of Energy
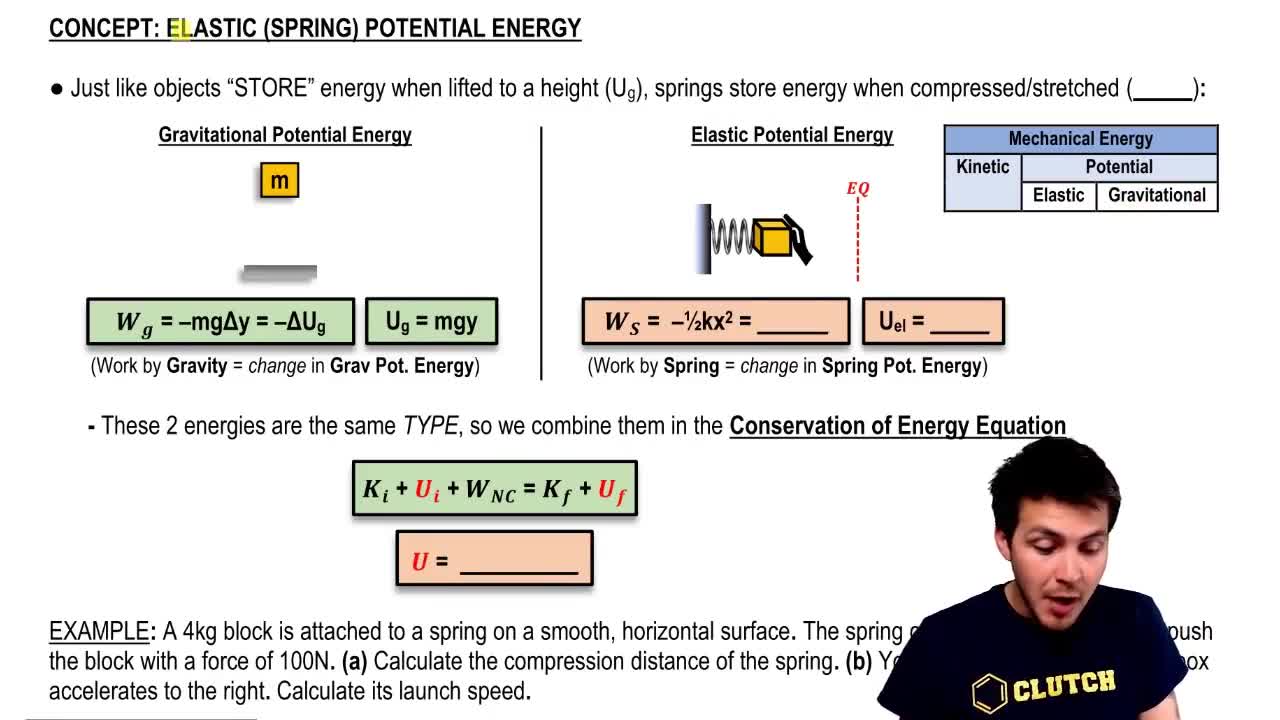
The principle of conservation of energy states that energy cannot be created or destroyed, only transformed from one form to another. In this scenario, the potential energy stored in the compressed spring is converted into gravitational potential energy as the ice cube moves up the slope. Understanding this concept is crucial for calculating the maximum height the ice cube reaches.
Recommended video:
Conservation Of Mechanical Energy
Spring Potential Energy
Spring potential energy is the energy stored in a compressed or stretched spring, calculated using the formula PE_spring = 1/2 k x^2, where k is the spring constant and x is the compression or extension from its equilibrium position. In this problem, the spring constant is given as 25 N/m, and the compression is 0.1 m, which allows us to determine the energy available to launch the ice cube.
Recommended video:
Energy in Horizontal Springs
Gravitational Potential Energy
Gravitational potential energy is the energy an object possesses due to its position in a gravitational field, expressed as PE_gravity = mgh, where m is mass, g is the acceleration due to gravity, and h is the height above a reference point. This concept is essential for calculating how high the ice cube rises after being launched by the spring, as it relates the energy from the spring to the height gained.
Recommended video:
Gravitational Potential Energy
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance