Here are the essential concepts you must grasp in order to answer the question correctly.
Work Done by Gravity
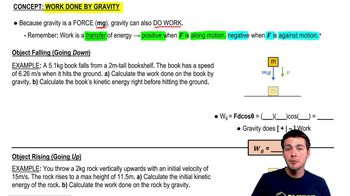
Work done by gravity is calculated using the formula W = mgh, where W is the work, m is the mass, g is the acceleration due to gravity (approximately 9.81 m/s²), and h is the height through which the object moves. In this context, the work done by gravity will be negative if the object is moving upward, as gravity opposes the motion.
Recommended video:
Kinetic Energy
Kinetic energy (KE) is the energy an object possesses due to its motion, given by the formula KE = 0.5mv², where m is the mass and v is the velocity. Understanding kinetic energy is essential for analyzing the changes in energy as the girder accelerates from 0.25 m/s to 0.75 m/s, which will help in determining the net work done on the girder.
Recommended video:
Intro to Rotational Kinetic Energy
Conservation of Energy
The principle of conservation of energy states that energy cannot be created or destroyed, only transformed from one form to another. In this scenario, the work done by gravity and the work done to accelerate the girder must balance out, allowing us to analyze how the potential energy lost by the girder as it rises relates to its change in kinetic energy.
Recommended video:
Conservation Of Mechanical Energy