Here are the essential concepts you must grasp in order to answer the question correctly.
Kinematics
Kinematics is the branch of mechanics that deals with the motion of objects without considering the forces that cause the motion. It involves concepts such as displacement, velocity, acceleration, and time. In this scenario, understanding kinematics is essential to calculate the distance traveled during the driver's reaction time and the subsequent braking distance.
Recommended video:
Acceleration and Deceleration
Acceleration refers to the rate of change of velocity of an object, while deceleration is a specific type of acceleration that indicates a decrease in speed. In this problem, the car's maximum deceleration of 10 m/s² is crucial for determining how quickly the car can stop after the brakes are applied. This concept helps in calculating the stopping distance once the brakes are engaged.
Recommended video:
Reaction Time
Reaction time is the interval between the perception of a stimulus and the initiation of a response. In this case, the driver's reaction time of 0.50 seconds is significant because it affects the total distance traveled before the brakes are applied. Understanding this concept is vital for accurately determining the total distance from the initial position to when the car comes to a complete stop.
Recommended video:
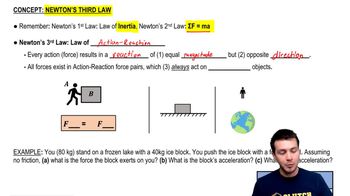
Newton's Third Law & Action-Reaction Pairs