Satellite Motion: Speed & Period definitions Flashcards
 Back
BackSatellite Motion: Speed & Period definitions
1/15
Terms in this set (15)
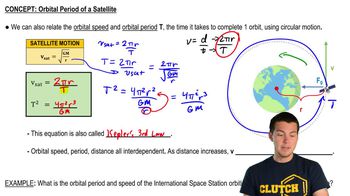
- Orbital SpeedThe velocity required for a satellite to maintain a stable circular orbit around a planet.
- Gravitational ConstantA universal constant (G) used in the calculation of gravitational forces between two masses.
- Orbital PeriodThe time it takes for a satellite to complete one full orbit around a planet.
- Centripetal AccelerationThe acceleration directed towards the center of a circular path, maintaining circular motion.
- Uniform Circular MotionMotion in a circular path at constant speed, requiring centripetal force.
- Kepler's Third LawA law relating the square of the orbital period to the cube of the orbital radius.
- Tangential VelocityThe component of velocity parallel to the circular path of a satellite.
- Orbital DistanceThe distance from the center of a planet to a satellite in orbit.
- International Space StationA satellite orbiting Earth at about 400 km, with a period of 1.5 hours and speed of 7660 m/s.
- Newton's Law of GravityA law stating the gravitational force between two masses is proportional to their product and inversely proportional to the square of their distance.
- CircumferenceThe distance around a circular path, calculated as 2π times the radius.
- Mass of the PlanetThe mass of the celestial body around which a satellite orbits, crucial for calculating orbital speed.
- Height Above EarthThe altitude of a satellite's orbit above Earth's surface, calculated using orbital parameters.
- Radius of the EarthThe distance from Earth's center to its surface, used in calculating satellite orbits.
- Orbital MechanicsThe study of the motion of satellites and celestial bodies under gravitational forces.