Heat Engines & PV Diagrams definitions Flashcards
 Back
BackHeat Engines & PV Diagrams definitions
1/15
Terms in this set (15)
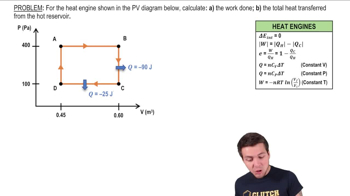
- PV DiagramA graphical representation of the pressure-volume relationship in thermodynamic processes.
- Heat EngineA device that converts thermal energy into mechanical work through cyclic processes.
- Cyclic ProcessA thermodynamic process that returns a system to its initial state, forming a closed loop on a PV diagram.
- Isobaric ProcessA thermodynamic process occurring at constant pressure.
- Isochoric ProcessA thermodynamic process occurring at constant volume, also known as isovolumetric.
- Isothermal ProcessA thermodynamic process occurring at constant temperature.
- WorkThe energy transferred by a system to its surroundings, often calculated as the area under a PV diagram curve.
- Energy Flow DiagramA schematic showing the flow of energy in a system, highlighting heat input, work output, and waste heat.
- Hot ReservoirThe source of heat energy input into a heat engine.
- Cold ReservoirThe sink where waste heat is expelled from a heat engine.
- Molar Specific HeatThe amount of heat required to raise the temperature of one mole of a substance by one degree Celsius.
- Monoatomic GasA gas consisting of single atoms, often used in thermodynamic calculations.
- Absolute ValueThe non-negative value of a number, used in calculations to ensure positive heat flow values.
- Clockwise LoopThe direction of a cycle on a PV diagram indicating a heat engine's operation.
- Delta TThe change in temperature, used in calculating heat transfer in thermodynamic processes.