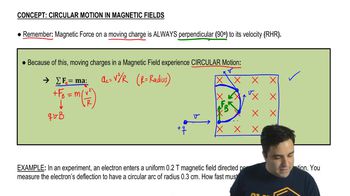
28. Magnetic Fields and Forces
Circular Motion of Charges in Magnetic Fields
28. Magnetic Fields and Forces
Circular Motion of Charges in Magnetic Fields
Additional 1 creators.
Learn with other creators
Practice this topic
- Textbook QuestionA beam of protons traveling at 1.20 km/s enters a uniform magnetic field, traveling perpendicular to the field. The beam exits the magnetic field, leaving the field in a direction perpendicular to its original direction (Fig. E27.24) . The beam travels a distance of 1.18 cm while in the field. What is the magnitude of the magnetic field?678views1rank
- Textbook QuestionIn a cyclotron, the orbital radius of protons with energy 300 keV is 16.0 cm. You are redesigning the cyclotron to be used instead for alpha particles with energy 300 keV. An alpha particle has charge q = +2e and mass m = 6.64x10^-27 kg. If the magnetic field isn't changed, what will be the orbital radius of the alpha particles?590views
- Textbook QuestionA deuteron (the nucleus of an isotope of hydrogen) has a mass of 3.34x10^-27 kg and a charge of +e. The deuteron travels in a circular path with a radius of 6.96 mm in a magnetic field with magnitude 2.50 T. (a) Find the speed of the deuteron. (b) Find the time required for it to make half a revolution. (c) Through what potential difference would the deuteron have to be accelerated to acquire this speed?958views
- Textbook QuestionCyclotrons are widely used in nuclear medicine for producing short-lived radioactive isotopes. These cyclotrons typically accelerate H- (the hydride ion, which has one proton and two electrons) to an energy of 5 MeV to 20 MeV. This ion has a mass very close to that of a proton because the electron mass is negligible—about 1/2000 of the proton's mass. A typical magnetic field in such cyclotrons is 1.9 T. (a) What is the speed of a 5.0-MeV H-? (b) If the H- has energy 5.0 MeV and B = 1.9 T, what is the radius of this ion's circular orbit?1818views1rank