19. Fluid Mechanics
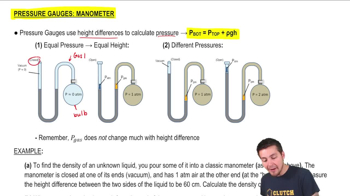
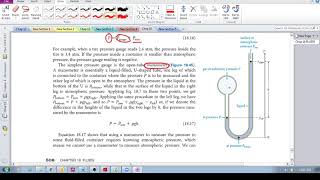
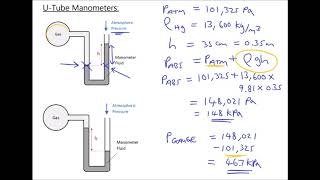
Pressure Gauge: Manometer
Learn with other creators
Practice this topic
- Multiple Choice
A classic manometer (as shown below) has one of its ends open, and a 2 atm gas on the other. When mercury (13,600 kg/m3 ) is added to the manometer, you measure the top of the mercury column on the left to be 40 cm higher than the mercury column on the right. Calculate the atmospheric pressure that the manometer is exposed to, in units of atm. (Use g=9.8 m/s2.)
987views8rank1comments - Textbook Question
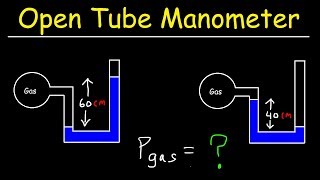
An open-tube mercury manometer is used to measure the pressure in an oxygen tank. When the atmospheric pressure is 1040 mbar, what is the absolute pressure (in Pa) in the tank if the height of the mercury in the open tube is 7.6 cm lower than the mercury in the tube connected to the tank? See Fig. 13–10a.
772views - Multiple Choice
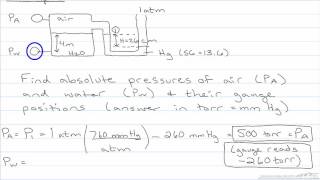
In a U-tube manometer connected to a gas tank, point 2 is located at the same horizontal level as the open end exposed to atmospheric pressure. If the height difference between the mercury columns is , the density of mercury is , and atmospheric pressure is , what is the gauge pressure at point 2?
48views - Multiple Choice
A U-tube manometer is connected to a gas tank. The left arm is open to the atmosphere, and the right arm is connected to the tank. The mercury level in the right arm is lower than in the left arm. If atmospheric pressure is , what does the top pressure gauge (connected to the tank) read?
35views - Multiple Choice
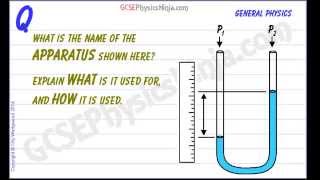
A U-tube manometer is filled with mercury and connected to four different gas containers. Which gas applies the most pressure to the manometer if the height difference between the mercury columns is as follows: Container A: , Container B: , Container C: , Container D: ?
43views