8. Centripetal Forces & Gravitation
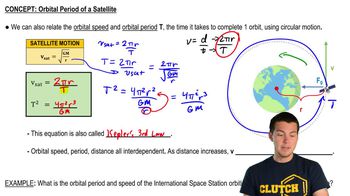
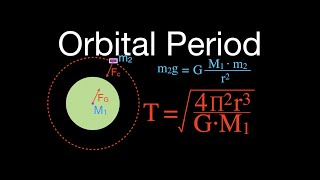
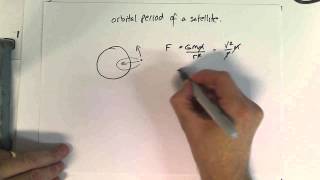
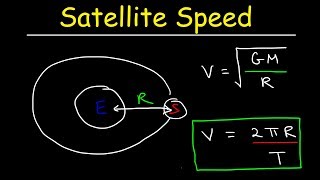
Satellite Motion: Speed & Period
Learn with other creators
Practice this topic
- Multiple Choice
Suppose that you used some geometry and kinematics to estimate that the Earth goes around the Sun with an orbital speed of approximately 30,000 m/s (60,000 mph), and that the Sun is approximately 150 million kilometers away from the Earth. Use this information to estimate the mass of the Sun.
1179views8rank1comments - Multiple Choice
You throw a baseball horizontally while on the surface of a small, spherical asteroid of mass 7×1016 kg and diameter of 22km. What is the minimum speed so that it just barely goes around the asteroid without hitting anything?
1139views15rank - Multiple Choice
A satellite orbits at an orbital period of 2 hours around the Moon. What is the satellite's orbital altitude?
1133views9rank1comments - Multiple Choice
A distant planet orbits a star 3 times the mass of our Sun. This planet of mass 8 × 1026 kg feels a gravitational force of 2 × 1026 N. What is this planet's orbital speed and how long does it take to orbit once?
1013views15rank5comments - Textbook Question
The Lunar Reconnaissance Orbiter (LRO) is a NASA Moon-orbiting spacecraft in an orbit with an altitude of 50 km above the Moon’s surface. What is the period of the LRO as it orbits the Moon?
974views - Textbook QuestionThree satellites orbit a planet of radius R, as shown in FIGUREEX13.24. Satellites S₁ and S₃ have mass m. Satellite S₂ has mass 2m. Satellite S₁ orbits in 250 minutes and the force on S₁ is 10,000 N.(b) What are the forces of S₂ and S₃?1623views
- Textbook Question
Three satellites orbit a planet of radius R, as shown in FIGURE EX13.24. Satellites S1 and S3 have mass m. Satellite S2 has mass 2m. Satellite S1 orbits in 250 minutes and the force on S1 is 10,000 N. What is the kinetic-energy ratio for K1 / K3 for S1 and S3?
1021views - Textbook Question
Large stars can explode as they finish burning their nuclear fuel, causing a supernova. The explosion blows away the outer layers of the star. According to Newton's third law, the forces that push the outer layers away have reaction forces that are inwardly directed on the core of the star. These forces compress the core and can cause the core to undergo a gravitational collapse. The gravitational forces keep pulling all the matter together tighter and tighter, crushing atoms out of existence. Under these extreme conditions, a proton and an electron can be squeezed together to form a neutron. If the collapse is halted when the neutrons all come into contact with each other, the result is an object called a neutron star, an entire star consisting of solid nuclear matter. Many neutron stars rotate about their axis with a period of ≈ 1 s and, as they do so, send out a pulse of electromagnetic waves once a second. These stars were discovered in the 1960s and are called pulsars. What is the radius of a geosynchronous orbit?
1419views