18. Waves & Sound
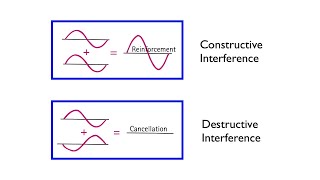
Wave Interference
Learn with other creators
Practice this topic
- Open Question
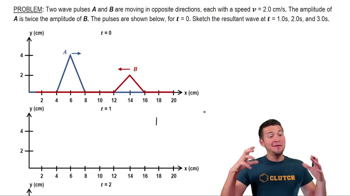
In the following figure, two interfering waves are drawn at some instance in time.
a. Indicate the regions on the graph where constructive interference occurs.
b.Indicate the regions on the graph where destructive interference occurs.713views5rank - Multiple ChoiceTwo sinusoidal waves with amplitudes and respectively, move toward each other on a string and experience superposition. As they move past each other, the displacement of the string from equilibrium is complicated. Considering all positions on the string where the waves are overlapping, what are the largest and smallest magnitudes of the displacement of the string?799views
- Multiple ChoiceSuppose you are listening to two tones, one of 50Hz, and the other of 10,000 Hz. If the sources of these tones are equal in intensity at your location, which do you perceive to have a higher sound intensity level (in dB), and by what factor?862views
- Multiple ChoiceYou are standing from one speaker and from another. Both are emitting identical 680Hz tones in phase. What best describes what you would observe? Use for the speed of sound.735views
- Multiple ChoiceTwo speakers (A and B) lie on the y-axis, apart. They emit exactly the same 280 Hz tone in phase with each other. You start right at speaker A and walk in the x-direction. How far from speaker A do you first hear a minimum in sound intensity? Assume the speed of sound in this room is944views
- Textbook Question
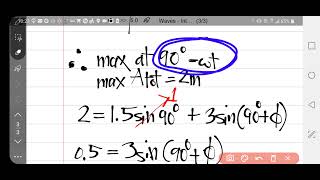
Small speakers A and B are driven in phase at 725 Hz by the same audio oscillator. Both speakers start out 4.50 m from the listener, but speaker A is slowly moved away (Fig. E16.34). At what distance d will the sound from the speakers first produce destructive interference at the listener's location?
<Image>
1625views - Textbook Question
Two loudspeakers, A and B (Fig. E16.35), are driven by the same amplifier and emit sinusoidal waves in phase. Speaker B is 2.00 m to the right of speaker A. Consider point Q along the extension of the line connecting the speakers, 1.00 m to the right of speaker B. Both speakers emit sound waves that travel directly from the speaker to point Q. What is the lowest frequency for which destructive interference occurs at point Q?
1213views - Textbook Question
Two loudspeakers, A and B (Fig. E16.35), are driven by the same amplifier and emit sinusoidal waves in phase. Speaker B is 2.00 m to the right of speaker A. Consider point Q along the extension of the line connecting the speakers, 1.00 m to the right of speaker B. Both speakers emit sound waves that travel directly from the speaker to point Q. What is the lowest frequency for which constructive interference occurs at point Q?
2188views