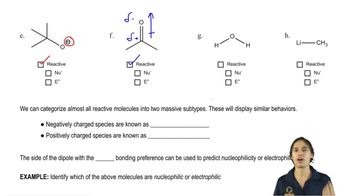
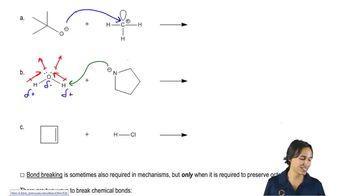
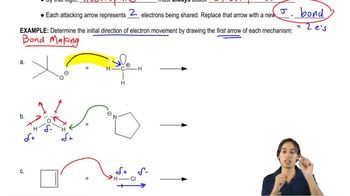
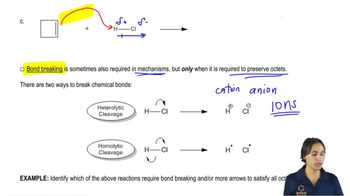
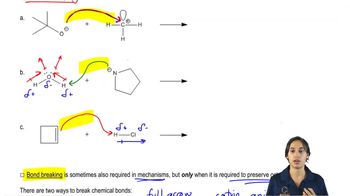
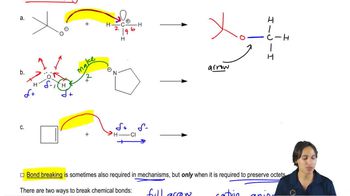
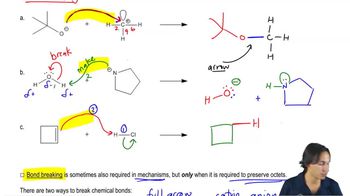
3. Acids and Bases
Reaction Mechanism
Practice this topic
- Multiple ChoiceWhat does it mean to be a nucleophile?538views
- Textbook Question
Each of these compounds can react as an electrophile. In each case, use curved arrows to show how the electrophile would react with the strong nucleophile sodium ethoxide, Na+ −OCH2CH3.
(c) CH3CH2Br
(d) BH3
655views - Textbook Question
In each reaction, label the reactants as Lewis acids (electrophiles) or Lewis bases (nucleophiles). Use curved arrows to show the movement of electron pairs in the reactions. Draw any nonbonding electrons to show how they participate in the reactions.
(b)
730views - Textbook Question
In each reaction, label the reactants as Lewis acids (electrophiles) or Lewis bases (nucleophiles). Use curved arrows to show the movement of electron pairs in the reactions. Draw any nonbonding electrons to show how they participate in the reactions.
(a)
812views - Textbook Question
Each of these compounds can react as a nucleophile. In each case, use curved arrows to show how the nucleophile would react with the strong electrophile BF3.
(a)
(b)
474views - Multiple ChoiceWhich of the following analogies best describes the induced-fit model of enzyme-substrate binding?129views
- Multiple ChoiceWhich graph best represents the energy profile of a reaction when an enzyme is present?210views
- Multiple ChoiceIn the context of reaction mechanisms, what do both the rho-dependent and rho-independent mechanisms of termination have in common?114views