Here are the essential concepts you must grasp in order to answer the question correctly.
Electrophilic Aromatic Substitution (EAS)
Electrophilic Aromatic Substitution is a fundamental reaction in organic chemistry where an electrophile replaces a hydrogen atom on an aromatic ring, such as benzene. This reaction is crucial for synthesizing various aromatic compounds, as it allows for the introduction of different functional groups onto the benzene ring, which can then be further modified to create complex molecules.
Recommended video:
Grignard Reagents
Grignard reagents are organomagnesium compounds that are highly reactive and used to form carbon-carbon bonds. They are synthesized by reacting magnesium with an alkyl or aryl halide. In the context of synthesizing 1-phenyl-2-propanol, a Grignard reagent can react with a carbonyl compound to produce an alcohol, demonstrating their utility in building larger organic molecules.
Recommended video:
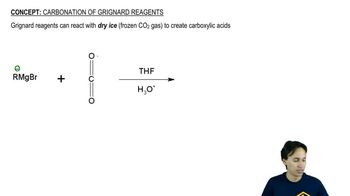
Carbonation of Grignard Reagents
Reduction Reactions
Reduction reactions involve the gain of electrons or the decrease in oxidation state of a molecule, often resulting in the formation of alcohols from carbonyl compounds. In the synthesis of 1-phenyl-2-propanol, a ketone or aldehyde intermediate can be reduced using reducing agents like lithium aluminum hydride (LiAlH4) or sodium borohydride (NaBH4) to yield the desired alcohol product.
Recommended video:
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance Verified video answer for a similar problem:
Verified video answer for a similar problem:

 2:49m
2:49m