Here are the essential concepts you must grasp in order to answer the question correctly.
Nuclear Magnetic Resonance (NMR) Spectroscopy
NMR spectroscopy is a powerful analytical technique used to determine the structure of organic compounds. It relies on the magnetic properties of certain nuclei, primarily hydrogen (1H), to provide information about the number of hydrogen atoms in different environments within a molecule. The resulting spectrum displays signals that correspond to these environments, allowing chemists to infer structural details.
Recommended video:
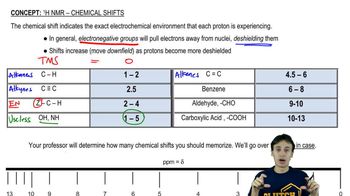
Chemical Shift
Chemical shift refers to the position of a signal in an NMR spectrum, which is influenced by the electronic environment surrounding the hydrogen atoms. Different functional groups and molecular structures can cause shifts in the resonance frequency of protons, leading to distinct signals. Understanding chemical shifts helps in identifying the types of hydrogen environments present in a compound.
Recommended video:
Multiplicity
Multiplicity in NMR refers to the splitting of a signal into multiple peaks, which occurs due to spin-spin coupling between neighboring hydrogen atoms. The number of peaks is determined by the n+1 rule, where n is the number of adjacent protons. This information provides insight into the number of neighboring hydrogens and helps in elucidating the connectivity and arrangement of atoms in the molecule.
Recommended video:
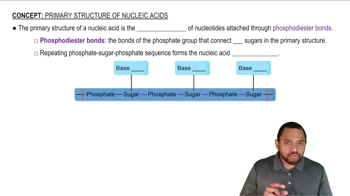
Primary Structure of Nucleic Acids Concept 1
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance Verified video answer for a similar problem:
Verified video answer for a similar problem:

 12:21m
12:21m