Here are the essential concepts you must grasp in order to answer the question correctly.
Elements of Unsaturation
Elements of unsaturation indicate the degree of saturation in a molecule, reflecting the presence of double bonds, triple bonds, or rings. Each double bond or ring contributes one element of unsaturation, while a triple bond contributes two. This concept is crucial for determining the structural possibilities of a compound based on its molecular formula.
Recommended video:
The difference between saturated and unsaturated molecules.
Molecular Formula Interpretation
A molecular formula, such as C4H9N, provides information about the number of each type of atom in a molecule. Understanding how to interpret this formula is essential for deducing the possible structures and their connectivity. The ratio of carbon, hydrogen, and nitrogen atoms helps in predicting the types of bonds and functional groups present.
Recommended video:
How to use IHD with molecular formula.
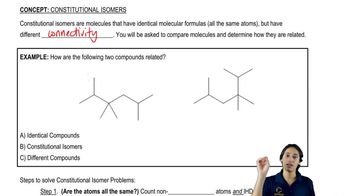
Structural Isomers
Structural isomers are compounds that share the same molecular formula but differ in the arrangement of atoms. For C4H9N, identifying all possible structures involves considering variations in connectivity, such as branching and functional group placement. Recognizing the concept of structural isomerism is vital for generating and naming the different valid structures for a given molecular formula.
Recommended video:
What is a constitutional isomer?
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance Verified Solution
Verified Solution


 1:10m
1:10m