Here are the essential concepts you must grasp in order to answer the question correctly.
Resonance Structures
Resonance structures are different ways of drawing the same molecule that illustrate the delocalization of electrons. They help in understanding the stability and reactivity of a molecule by showing how electrons can be distributed across different atoms. In organic chemistry, resonance is crucial for predicting the behavior of cations and anions, as it can stabilize charges through electron sharing.
Recommended video:
Drawing Resonance Structures
Cation and Anion Stability
Cations (positively charged species) and anions (negatively charged species) exhibit different stabilities based on their electronic environments. Cations are generally stabilized by electron-donating groups, while anions are stabilized by electron-withdrawing groups. Understanding the factors that influence the stability of these charged species is essential for predicting their reactivity and the formation of resonance structures.
Recommended video:
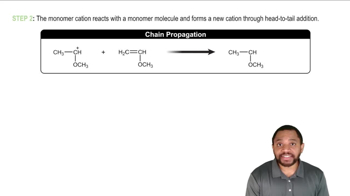
Cationic Polymerization Concept 3
Electron Delocalization
Electron delocalization refers to the spreading of electron density across multiple atoms in a molecule, which can lower the overall energy and increase stability. This phenomenon is particularly important in resonance structures, where electrons are not confined to a single bond or atom. Recognizing how delocalization occurs helps in drawing accurate resonance forms and understanding the properties of organic compounds.
Recommended video:
The 18 and 16 Electron Rule


 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance Verified video answer for a similar problem:
Verified video answer for a similar problem:


 3:34m
3:34m