Here are the essential concepts you must grasp in order to answer the question correctly.
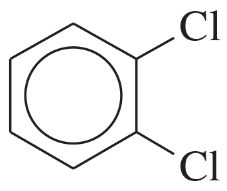
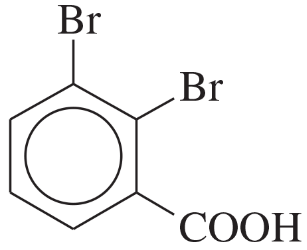
Nomenclature of Aromatic Compounds
Aromatic compounds, such as benzene derivatives, follow specific naming conventions established by IUPAC. The base name is derived from the parent aromatic compound, with substituents indicated by prefixes. The position of substituents is denoted by numbers or letters (ortho, meta, para) based on their relative positions on the benzene ring.
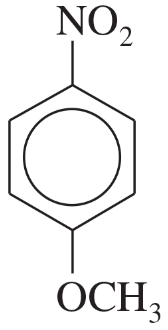
Substituent Effects
Substituents on a benzene ring can influence the reactivity and orientation of further substitutions due to their electronic effects. Electron-donating groups (EDGs) such as -OCH3 activate the ring towards electrophilic substitution, while electron-withdrawing groups (EWGs) like -NO2 deactivate it and direct incoming substituents to specific positions on the ring.
Ortho, Meta, and Para Positions
The terms ortho, meta, and para describe the relative positions of substituents on a benzene ring. Ortho refers to substituents on adjacent carbons, meta to those separated by one carbon, and para to those opposite each other. Understanding these positions is crucial for correctly naming compounds and predicting their chemical behavior.
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance Verified video answer for a similar problem:
Verified video answer for a similar problem: