Here are the essential concepts you must grasp in order to answer the question correctly.
Tollens Test
The Tollens test is a qualitative test used to identify aldehydes and certain ketones. It involves the use of Tollens' reagent, which contains silver nitrate in ammonia, and reacts with aldehydes to produce a silver mirror on the test tube. This reaction occurs under mild basic conditions, making it a useful method for distinguishing between different types of carbonyl compounds.
Recommended video:
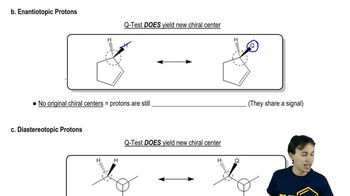
Q-Test (Proton Relationships)
Aldehydes vs. Ketones
Aldehydes are organic compounds characterized by the presence of a carbonyl group (C=O) at the end of a carbon chain, while ketones have the carbonyl group located within the chain. Aldehydes are generally more reactive than ketones in nucleophilic addition reactions, which is why they can be easily oxidized and detected by the Tollens test, whereas most ketones do not react under these conditions.
Recommended video:
Nucleophilic Addition on Ketones and Aldehydes
Mild Basic Conditions
Mild basic conditions refer to a slightly alkaline environment that facilitates certain chemical reactions without causing excessive reactivity or decomposition. In the context of the Tollens test, these conditions help stabilize the Tollens reagent and promote the oxidation of aldehydes while preventing unwanted side reactions that could interfere with the test results.
Recommended video:
Understanding the difference between basicity and nucleophilicity.
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance Verified video answer for a similar problem:
Verified video answer for a similar problem: