Here are the essential concepts you must grasp in order to answer the question correctly.
Acid-Base Equilibrium
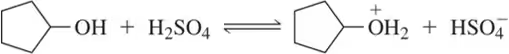
Acid-base equilibrium refers to the state in which the rates of the forward and reverse reactions of an acid and its conjugate base are equal. This equilibrium can be quantified using the equilibrium constant (K_eq), which expresses the ratio of the concentrations of products to reactants at equilibrium. Understanding this concept is crucial for calculating K_eq in acid-base reactions.
Recommended video:
Determining Acid/Base Equilibrium
pKₐ and Kₐ Relationship
The pKₐ is a logarithmic scale that indicates the strength of an acid, with lower values corresponding to stronger acids. It is related to the acid dissociation constant (Kₐ) by the equation pKₐ = -log(Kₐ). This relationship is essential for determining the equilibrium constant (K_eq) in acid-base reactions, as it allows for the conversion between pKₐ values and Kₐ values.
Recommended video:
Common Acid-Base Reactions
Common acid-base reactions involve the transfer of protons (H⁺) between acids and bases. Familiarity with these reactions, including the identification of strong and weak acids and bases, is vital for predicting the direction of equilibrium and calculating K_eq. Recognizing the common acids and their pKₐ values helps streamline the process of determining the equilibrium constant in various reactions.
Recommended video:
The Lewis definition of acids and bases.
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance Verified video answer for a similar problem:
Verified video answer for a similar problem:



 1:46m
1:46m