Here are the essential concepts you must grasp in order to answer the question correctly.
Constitutional Isomers
Constitutional isomers are compounds that have the same molecular formula but differ in the connectivity of their atoms. This means that the arrangement of atoms in the molecule varies, leading to different structural forms. For example, C₅H₁₂O can have various isomers based on how the carbon, hydrogen, and oxygen atoms are connected.
Recommended video:
What is a constitutional isomer?
Functional Isomers
Functional isomers are a type of constitutional isomer where the isomers differ in the functional group present in the molecule. For instance, in C₅H₁₂O, one isomer could be an alcohol (like pentanol) while another could be an ether (like dimethyl ether), showcasing how the same atoms can form different functional groups.
Recommended video:
What is a constitutional isomer?
Positional and Chain Isomers
Positional isomers occur when the position of a functional group changes within the same carbon skeleton, while chain isomers arise from variations in the carbon chain structure, such as branching. In C₅H₁₂O, different placements of the hydroxyl group in pentanol or variations in the carbon chain can lead to distinct isomers, illustrating the diversity of structures possible with the same molecular formula.
Recommended video:
What is a constitutional isomer?
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance Verified Solution
Verified Solution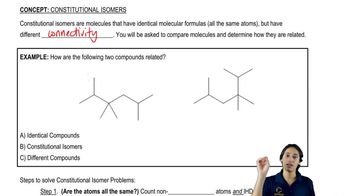



 1:10m
1:10m