Here are the essential concepts you must grasp in order to answer the question correctly.
Condensed Structural Formula
A condensed structural formula is a way of representing a chemical compound that shows the arrangement of atoms and the connectivity between them without depicting all the bonds explicitly. In this format, groups of atoms are often grouped together to simplify the structure, making it easier to visualize larger molecules. For example, in a condensed formula, 'C2H5' represents an ethyl group, indicating two carbon atoms and five hydrogen atoms.
Recommended video:
How to interpret condensed structures.
Alkynes
Alkynes are a class of hydrocarbons characterized by at least one carbon-carbon triple bond. They follow the general formula CnH2n-2, where 'n' is the number of carbon atoms. The presence of the triple bond gives alkynes unique chemical properties, including increased reactivity compared to alkenes and alkanes. Understanding the structure and reactivity of alkynes is essential for drawing their condensed formulas accurately.
Recommended video:
Tertiary Alkyl Groups
Tertiary alkyl groups are carbon groups where the central carbon atom is bonded to three other carbon atoms. This structure significantly influences the stability and reactivity of the compound. In the context of di-tert-butylacetylene, the presence of two tert-butyl groups (C4H9) attached to the acetylene backbone affects the overall molecular structure and properties, making it crucial to recognize these groups when drawing condensed structures.
Recommended video:
Tertiary Protein Structure Example 1
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance Verified video answer for a similar problem:
Verified video answer for a similar problem: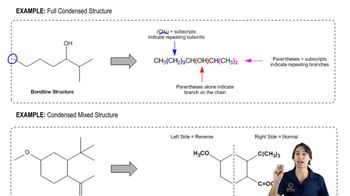



 1:55m
1:55m