Here are the essential concepts you must grasp in order to answer the question correctly.
1H NMR Spectroscopy
Proton Nuclear Magnetic Resonance (1H NMR) spectroscopy is a powerful analytical technique used to determine the structure of organic compounds. It provides information about the number of hydrogen atoms in different environments, their chemical shifts (ppm), and the splitting patterns, which indicate the number of neighboring hydrogen atoms. Understanding these signals helps in deducing the molecular structure and connectivity of the compound.
Recommended video:
Chemical Shifts and Splitting Patterns
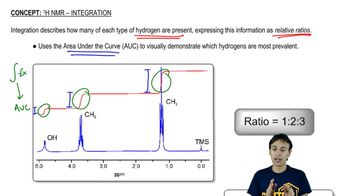
In 1H NMR, chemical shifts are measured in parts per million (ppm) and indicate the electronic environment of hydrogen atoms. For example, a doublet suggests that a hydrogen atom is adjacent to one other hydrogen, while a quartet indicates three neighboring hydrogens. The specific chemical shifts and splitting patterns provide clues about the functional groups and the overall structure of the compound being analyzed.
Recommended video:
Common Splitting Patterns
Molecular Formula Interpretation
The molecular formula provides essential information about the number and types of atoms in a compound. For C8H9Br, the formula indicates the presence of 8 carbon atoms, 9 hydrogen atoms, and 1 bromine atom. This information, combined with NMR data, allows chemists to deduce possible structures and identify the compound by matching the spectral data with known compounds.
Recommended video:
How to use IHD with molecular formula.
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance Verified Solution
Verified Solution