Here are the essential concepts you must grasp in order to answer the question correctly.
Acetylene Reactivity
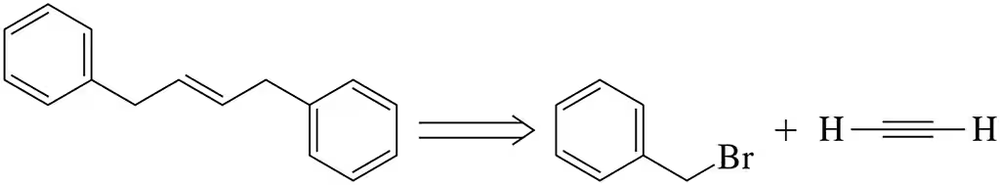
Acetylene (C2H2) is a simple alkyne that can undergo various reactions due to its triple bond. It can participate in nucleophilic addition reactions, where it acts as a nucleophile, and can also be converted into more complex structures through coupling reactions. Understanding its reactivity is crucial for designing synthetic pathways involving acetylene.
Recommended video:
Nucleophilic Substitution
Nucleophilic substitution is a fundamental reaction in organic chemistry where a nucleophile replaces a leaving group in a molecule. In the context of benzyl bromide, the bromine atom serves as a leaving group, allowing nucleophiles to attack the carbon atom bonded to it. This concept is essential for understanding how to manipulate benzyl bromide in the synthesis process.
Recommended video:
Nucleophiles and Electrophiles can react in Substitution Reactions.
Alkene Formation
Alkene formation is a key transformation in organic synthesis, often achieved through elimination reactions or coupling reactions. In this case, the goal is to form a double bond between carbon atoms, which can be accomplished by removing elements from adjacent carbon atoms. Recognizing the mechanisms and conditions that favor alkene formation is vital for successfully proposing a synthetic route.
Recommended video:
Alkene Metathesis Concept 1
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance Verified video answer for a similar problem:
Verified video answer for a similar problem:



 3:25m
3:25m