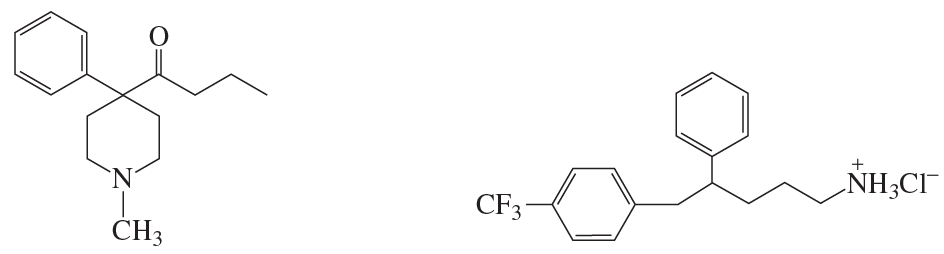
Here are the essential concepts you must grasp in order to answer the question correctly.
Hybridization
Hybridization is the concept in organic chemistry that describes the mixing of atomic orbitals to form new hybrid orbitals. These hybrid orbitals are used to form covalent bonds in molecules. The type of hybridization (sp, sp2, sp3) depends on the number of bonds and lone pairs around the atom, influencing the geometry and reactivity of the compound.
Recommended video:
Using bond sites to predict hybridization
Valence Shell Electron Pair Repulsion (VSEPR) Theory
VSEPR theory is a model used to predict the geometry of individual molecules based on the repulsion between electron pairs in the valence shell of the central atom. It helps determine the spatial arrangement of atoms in a molecule, which is crucial for understanding hybridization and molecular shape, particularly for carbon, nitrogen, and oxygen in organic compounds.
Recommended video:
Valence Electrons of Transition Metals
Functional Groups
Functional groups are specific groups of atoms within molecules that are responsible for the characteristic chemical reactions of those molecules. In the context of the given compounds, understanding the functional groups (like amines, alcohols, and ethers) is essential for determining the hybridization of the involved atoms, as they influence the bonding and electronic environment.
Recommended video:
Identifying Functional Groups
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance Verified video answer for a similar problem:
Verified video answer for a similar problem:



 2:53m
2:53m