Here are the essential concepts you must grasp in order to answer the question correctly.
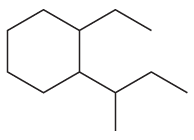
Primary Carbons
Primary carbons are carbon atoms that are bonded to only one other carbon atom. They are typically found at the ends of carbon chains or branches. In organic compounds, identifying primary carbons is crucial for understanding the structure and reactivity of the molecule.
Recommended video:
Primary Protein Structure Example 1
Secondary Carbons
Secondary carbons are carbon atoms that are bonded to two other carbon atoms. These carbons are often located in the middle of carbon chains or branches. Recognizing secondary carbons is important for predicting the behavior of the compound during chemical reactions, especially in substitution and elimination processes.
Recommended video:
Secondary Protein Structure Concept 1
Tertiary Carbons
Tertiary carbons are carbon atoms that are bonded to three other carbon atoms. They are typically found in branched structures and play a significant role in the stability and reactivity of organic compounds. Understanding tertiary carbons is essential for grasping concepts like carbocation stability and reaction mechanisms.
Recommended video:
Tertiary Protein Structure Concept 1
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance Verified video answer for a similar problem:
Verified video answer for a similar problem:

 1:49m
1:49m