Here are the essential concepts you must grasp in order to answer the question correctly.
Radical Formation
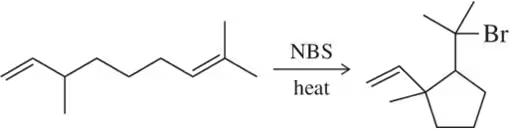
Radical formation involves the homolytic cleavage of a covalent bond, resulting in two radicals, each possessing an unpaired electron. This process is typically initiated by heat or light, which provides the energy needed to break the bond. Understanding how radicals are generated is crucial for predicting the behavior and reactivity in radical reactions.
Recommended video:
Radical Polymerization Concept 4
Propagation Steps
Propagation steps in radical reactions involve the radicals reacting with stable molecules to form new radicals, perpetuating the reaction cycle. These steps are essential for the continuation of the radical chain reaction, where the radical species generated in one step react further to produce additional radicals, driving the reaction forward until termination.
Recommended video:
Step-Growth Polymers Concept 1
Termination Steps
Termination steps occur when two radical species combine to form a stable, non-radical product, effectively ending the radical chain reaction. This can happen through various pathways, such as radical recombination or disproportionation. Understanding termination is key to controlling radical reactions and preventing unwanted side reactions or polymerization.
Recommended video:
Step-Growth Polymers Concept 1
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance Verified video answer for a similar problem:
Verified video answer for a similar problem: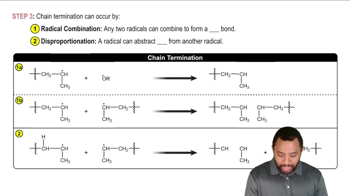


 6:15m
6:15m