Here are the essential concepts you must grasp in order to answer the question correctly.
Carbonyl Compounds
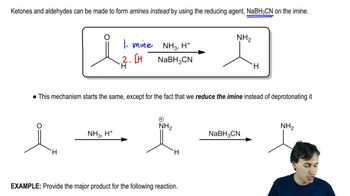
Carbonyl compounds contain a carbon atom double-bonded to an oxygen atom (C=O). This functional group is pivotal in organic chemistry, as it is involved in various reactions, including the formation of imines. Common examples include aldehydes and ketones, which can react with amines to form imines through a condensation reaction, releasing water.
Recommended video:
Amines
Amines are organic compounds derived from ammonia (NH3) by replacing one or more hydrogen atoms with alkyl or aryl groups. They can act as nucleophiles due to the lone pair of electrons on the nitrogen atom, allowing them to react with carbonyl compounds to form imines. Amines can be classified as primary, secondary, or tertiary based on the number of carbon groups attached to the nitrogen.
Recommended video:
Imines
Imines are compounds characterized by a carbon-nitrogen double bond (C=N), formed when a carbonyl compound reacts with an amine. This reaction typically involves the nucleophilic attack of the amine on the carbonyl carbon, followed by dehydration. Imines are important intermediates in organic synthesis and can undergo further reactions, such as hydrolysis or reduction.
Recommended video:
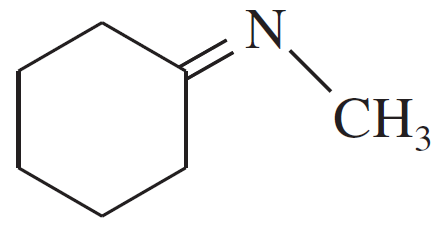
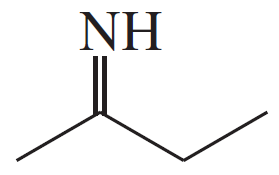
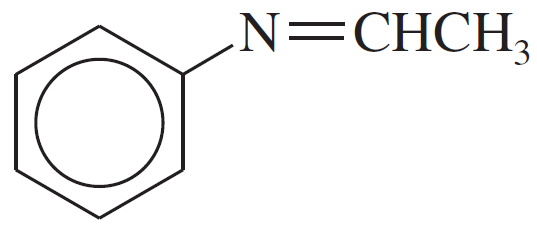
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance Verified video answer for a similar problem:
Verified video answer for a similar problem: