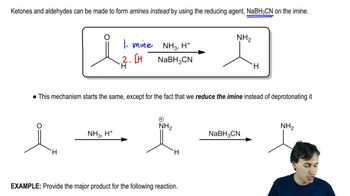
Here are the essential concepts you must grasp in order to answer the question correctly.
Electrophilic Aromatic Substitution (EAS)
Electrophilic Aromatic Substitution is a fundamental reaction in organic chemistry where an electrophile replaces a hydrogen atom on an aromatic ring. This reaction is crucial for synthesizing various aromatic compounds, including those derived from benzene and toluene. Understanding the mechanism of EAS, including the role of activating and deactivating groups, is essential for predicting the products of reactions involving aromatic compounds.
Recommended video:
N-Alkylation of Amines
N-Alkylation of amines involves the introduction of an alkyl group to the nitrogen atom of an amine, forming a substituted amine. This reaction is typically carried out using alkyl halides or other alkylating agents. In the context of synthesizing N-benzylpropan-1-amine, understanding how to effectively perform this reaction is vital, especially when considering regioselectivity and the potential for side reactions.
Recommended video:
Synthesis of Amines from Alcohols
The conversion of alcohols to amines can be achieved through various methods, including reduction and substitution reactions. In this synthesis, alcohols can be transformed into amines via nucleophilic substitution or by using reagents that facilitate the formation of amines. Recognizing the appropriate conditions and reagents for these transformations is key to successfully synthesizing compounds like N-benzylpropan-1-amine from the specified starting materials.
Recommended video:
Forming alcohols through SN2 reactions.
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance Verified video answer for a similar problem:
Verified video answer for a similar problem: