Here are the essential concepts you must grasp in order to answer the question correctly.
Intramolecular Reactions
Intramolecular reactions occur within a single molecule, allowing reactive groups to come into close proximity. This proximity increases the likelihood of successful collisions between reactants, leading to a higher reaction rate. Additionally, intramolecular reactions often benefit from reduced entropic penalties compared to intermolecular reactions, making them thermodynamically more favorable.
Recommended video:
Rates of Intramolecular Reactions Concept 1
Cyclization
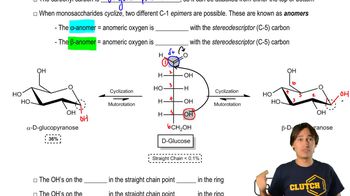
Cyclization refers to the process of forming a cyclic compound from a linear precursor. In organic chemistry, this often involves the formation of rings through the reaction of functional groups within the same molecule. The stability of the resulting cyclic structure can be influenced by factors such as ring strain and the nature of the substituents involved.
Recommended video:
Monosaccharides - Cyclization
Reaction Mechanism
A reaction mechanism describes the step-by-step sequence of elementary reactions that occur during a chemical transformation. Understanding the mechanism is crucial for predicting the products of a reaction, as it reveals how bonds are broken and formed. In the context of cyclization, knowing the mechanism helps in anticipating the stereochemistry and regioselectivity of the final product.
Recommended video:
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance Verified Solution
Verified Solution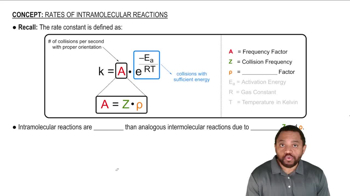


 9:36m
9:36m