Here are the essential concepts you must grasp in order to answer the question correctly.
Isomerism
Isomerism refers to the phenomenon where two or more compounds have the same molecular formula but different structural arrangements or spatial orientations. This can lead to variations in physical and chemical properties. Understanding isomerism is crucial for distinguishing between different types of compounds and their reactivity.
Recommended video:
Monosaccharides - D and L Isomerism
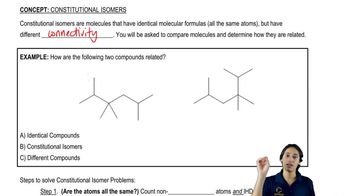
Constitutional Isomers
Constitutional isomers are a type of isomerism where compounds have the same molecular formula but differ in the connectivity of their atoms. This means that the atoms are bonded in different orders, leading to distinct structural forms. The example in the question illustrates two constitutional isomers, a pentagon (cyclopentane) and a square (cyclobutane), which have different shapes and properties despite having the same number of carbon and hydrogen atoms.
Recommended video:
What is a constitutional isomer?
Structural Representation
Structural representation is a way of depicting the arrangement of atoms within a molecule. It provides insight into the connectivity and geometry of the compound. In the context of the question, the structural representations of the pentagon and square help identify them as constitutional isomers, highlighting how different arrangements of the same atoms can lead to distinct molecular structures.
Recommended video:
Representations of L-Configuration

 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance Verified Solution
Verified Solution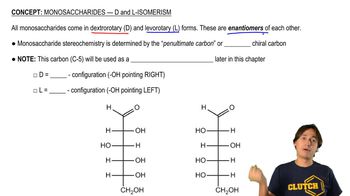


 1:10m
1:10m