Here are the essential concepts you must grasp in order to answer the question correctly.
Aerobic and Anaerobic Processes
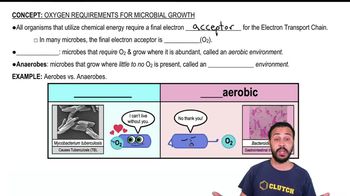
Aerobic processes require oxygen to occur, while anaerobic processes do not. In microbiology, these terms are crucial for understanding how different microorganisms metabolize substrates. For instance, aerobic bacteria thrive in environments with ample oxygen, leading to efficient breakdown of organic matter, whereas anaerobic bacteria perform fermentation or other metabolic processes in oxygen-deprived conditions.
Recommended video:
Activated Sludge System
An activated sludge system is a wastewater treatment process that uses aeration and a biological floc composed of microorganisms to degrade organic pollutants. This system typically operates under aerobic conditions, where oxygen is supplied to promote the growth of aerobic bacteria, which effectively break down waste materials. Understanding this system is essential for determining the conditions under which it operates.
Recommended video:
Oxygen's Role in Microbial Metabolism
Oxygen plays a critical role in microbial metabolism, influencing the types of metabolic pathways that microorganisms can utilize. In aerobic conditions, organisms can perform cellular respiration, yielding more energy compared to anaerobic processes like fermentation. The presence or absence of oxygen can significantly affect the efficiency of waste treatment processes, such as those in activated sludge systems.
Recommended video:
Oxygen Requirements for Microbial Growth