DRAW IT Show where airborne microbes ended up in Pasteur’s experiment. <IMAGE>
Use the following choices to answer questions 9 and 10.
1. 9 + 2 flagella
2. 70s ribosome
3. fimbria
4. nucleus
5. peptidoglycan
6. plasma membrane
Which is (are) found only in prokaryotes?
a. 1,4,6
b. 3,5
c. 1,2
d. 4
e. 2,4,5
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance
Verified video answer for a similar problem:
Key Concepts
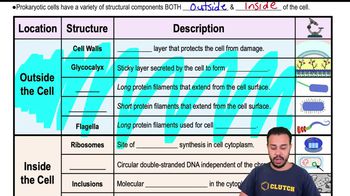
Prokaryotic Cell Structure
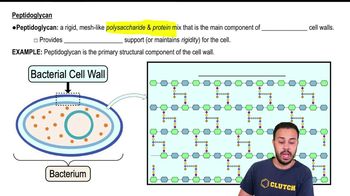
Peptidoglycan
Ribosome Differences

Which of the following is an example of bioremediation?
a. application of oil-degrading bacteria to an oil spill
b. application of bacteria to a crop to prevent frost damage
c. fixation of gaseous nitrogen into usable nitrogen
d. production by bacteria of a human protein such as interferon
e. all of the above
Spallanzani’s conclusion about spontaneous generation was challenged because Antoine Lavoisier had just shown that oxygen was the vital component of air. Which of the following statements is true?
a. All life requires air.
b. Only disease-causing organisms require air.
c. Some microbes do not require air.
d. Pasteur kept air out of his biogenesis experiments.
e. Lavoisier was mistaken.
Bergey’s Manual of Systematics of Archaea and Bacteria differs from Bergey’s Manual of Determinative Bacteriology in that the former
a. groups bacteria into species.
b. groups bacteria according to phylogenetic relationships.
c. groups bacteria according to pathogenic properties.
d. groups bacteria into 19 species.
e. all of the above
Bacillus and Lactobacillus are not in the same order. This indicates that which one of the following is not sufficient to assign an organism to a taxon?
a. biochemical characteristics
b. amino acid sequencing
c. phage typing
d. serology
e. morphological characteristics
Which of the following is used to classify organisms into the Kingdom Fungi?
a. ability to photosynthesize; possess a cell wall
b. unicellular; possess cell wall; prokaryotic
c. unicellular; lacking cell wall; eukaryotic
d. absorptive; possess cell wall; eukaryotic
e. ingestive; lacking cell wall; multicellular; prokaryotic
