Here are the essential concepts you must grasp in order to answer the question correctly.
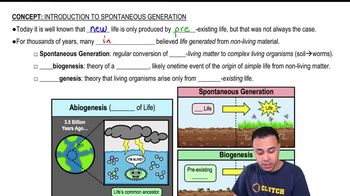
Spontaneous Generation
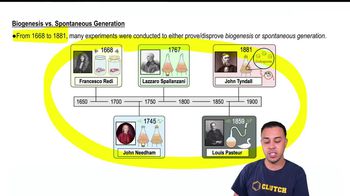
Spontaneous generation is the discredited theory that living organisms can arise from non-living matter without the involvement of reproduction. Historically, it was believed that life could spontaneously emerge from decaying organic material. This concept was challenged by experiments conducted by scientists like Louis Pasteur, who demonstrated that microorganisms come from other microorganisms, not from spontaneous generation.
Recommended video:
Introduction to Spontaneous Generation
Role of Oxygen in Life
Oxygen is a critical component of cellular respiration, a process by which many organisms, including humans and many microbes, convert nutrients into energy. Antoine Lavoisier's work established that oxygen is essential for combustion and respiration, leading to the understanding that many forms of life require oxygen to survive. However, some organisms, known as anaerobes, can thrive in environments devoid of oxygen.
Recommended video:
Biogenesis vs. Abiogenesis
Biogenesis is the principle that living organisms arise from pre-existing life, contrasting with abiogenesis, which suggests that life can originate from non-living matter. The debate between these two concepts was pivotal in microbiology, particularly through the experiments of Pasteur, who provided evidence for biogenesis by showing that sterilized broth remained free of microbial life when protected from contamination, thus supporting the idea that life comes from existing life.
Recommended video:
Biogenesis vs. Spontaneous Generation