Here are the essential concepts you must grasp in order to answer the question correctly.
Transformation
Transformation is a process by which bacteria take up free DNA from their environment and incorporate it into their own genome. This can occur naturally in some bacterial species, allowing them to acquire new traits, such as antibiotic resistance. The uptake of DNA can be facilitated by specific proteins on the bacterial cell surface that recognize and bind to the DNA.
Recommended video:
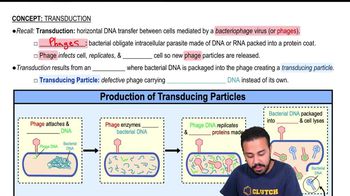
Transduction
Transduction is a method of horizontal gene transfer in bacteria that involves the transfer of DNA from one bacterium to another via a bacteriophage, or virus that infects bacteria. During this process, the bacteriophage can accidentally incorporate bacterial DNA into its own genome and transfer it to a new host during infection. This mechanism can lead to genetic diversity and the spread of traits among bacterial populations.
Recommended video:
Conjugation
Conjugation is a direct transfer of genetic material between two bacterial cells that are temporarily joined. This process typically involves a donor cell with a plasmid, which is a small circular DNA molecule, and a recipient cell. The donor forms a physical connection, often through a structure called a pilus, allowing the plasmid to be transferred, which can confer advantageous traits such as antibiotic resistance.
Recommended video:
Introduction to Conjugation
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance