On the following photos, label cilium, flagellum, nucleus, and pseudopod.
<IMAGE>
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance

On the following photos, label cilium, flagellum, nucleus, and pseudopod.
<IMAGE>
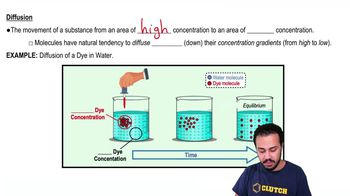
A cell may allow a large or charged chemical to move across the cytoplasmic membrane, down the chemical’s electrical and chemical gradients, in a process called _________ . .
a. active transport
b. facilitated diffusion
c. endocytosis
d. pinocytosis
Which cellular structure is important in classifying a bacterial species as Gram positive or Gram negative?
a. flagella
b. cell wall
c. cilia
d. glycocalyx
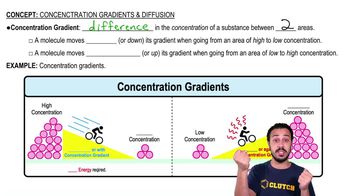
Match the structures with their descriptions following. A letter may be used more than once or not at all, and more than one letter may be correct for each blank.
____ Glycocalyx
____ Flagella
____ Axial filaments
____ Cilia
____ Fimbriae
____ Pili
____ Hami
A. Bristlelike projections found in quantities of 100 or more
B. Long whip
C. Responsible for conjugation
D. “Sweet cup” composed of polysaccharides and/or polypeptides
E. Numerous “grappling-hook” projections
F. Responsible for motility of spirochetes
G. Extensions not used for cell motility
H. Made of tubulin in eukaryotes
I. Made of flagellin in bacteria
Label the structures of the following prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells. With a single word or short phrase, explain the function of each structure.
<IMAGE> <IMAGE>
a. h.
b. i.
c. j.
d. k.
e. l.
f. m.
g. n.
o.
p.
q.