Here are the essential concepts you must grasp in order to answer the question correctly.
Amino Acid Biosynthesis
Amino acid biosynthesis refers to the metabolic pathways through which cells synthesize amino acids, the building blocks of proteins. In plants and microorganisms, this process often involves complex pathways that convert simple precursors into amino acids, such as tryptophan, tyrosine, and phenylalanine, which are essential for various biological functions.
Recommended video:
Erythrose 4-Phosphate
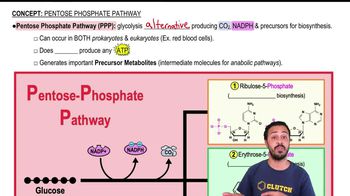
Erythrose 4-phosphate is a four-carbon sugar phosphate that plays a crucial role in the pentose phosphate pathway and is a precursor in the biosynthesis of aromatic amino acids. It is derived from glucose-6-phosphate and is involved in the shikimic acid pathway, which leads to the production of tryptophan, tyrosine, and phenylalanine.
Recommended video:
Pentose-Phosphate Pathway
Phosphoenolpyruvate (PEP)
Phosphoenolpyruvate (PEP) is a key intermediate in several metabolic pathways, including glycolysis and the biosynthesis of aromatic amino acids. It is produced from pyruvate and is essential for the shikimic acid pathway, where it combines with erythrose 4-phosphate to initiate the synthesis of aromatic amino acids, highlighting its importance in cellular metabolism.
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance Verified Solution
Verified Solution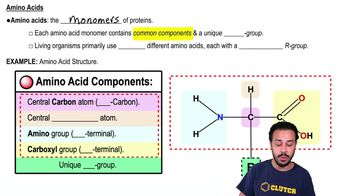

 4:44m
4:44m