Here are the essential concepts you must grasp in order to answer the question correctly.
Quaternary Ammonium Compounds (Quats)
Quaternary ammonium compounds are a class of disinfectants known for their ability to kill a wide range of microorganisms, particularly gram-positive bacteria. They function by disrupting microbial cell membranes, leading to cell lysis. Commonly used in various cleaning and sanitizing products, quats are effective against bacteria and some viruses but have limitations against spores and certain fungi.
Recommended video:
Bactericidal vs. Sporicidal
Bactericidal agents are substances that kill bacteria, while sporicidal agents specifically target bacterial spores, which are resistant forms of bacteria. Quaternary ammonium compounds are generally bactericidal but are not classified as sporicidal, meaning they do not effectively kill spores. Understanding this distinction is crucial when evaluating the effectiveness of disinfectants in different contexts.
Recommended video:
Spectrum of Activity
The spectrum of activity refers to the range of microorganisms that a disinfectant or antimicrobial agent can effectively kill or inhibit. Quaternary ammonium compounds are effective against a variety of pathogens, including gram-positive bacteria and enveloped viruses, but their efficacy against fungi and spores is limited. Recognizing the spectrum of activity helps in selecting the appropriate disinfectant for specific applications.
Recommended video:
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance Verified Solution
Verified Solution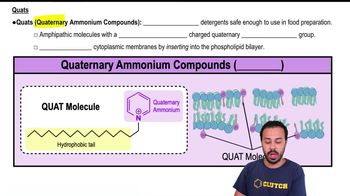

 4:14m
4:14m