Here are the essential concepts you must grasp in order to answer the question correctly.
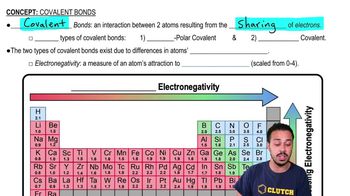
Covalent Bonds
Covalent bonds are chemical bonds formed when two atoms share one or more pairs of electrons. This sharing allows each atom to attain a full outer shell of electrons, leading to greater stability. Covalent bonds can be single, double, or triple, depending on the number of shared electron pairs. They are typically strong and are fundamental in forming molecules.
Recommended video:
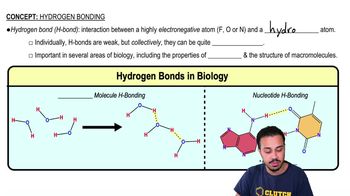
Hydrogen Bonds
Hydrogen bonds are weak attractions that occur between a hydrogen atom covalently bonded to an electronegative atom and another electronegative atom. These bonds are crucial in determining the properties of water and the structure of proteins and nucleic acids. Although weaker than covalent bonds, hydrogen bonds play a significant role in the stability and functionality of biological molecules.
Recommended video:
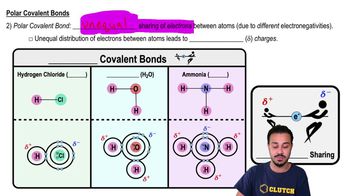
Polar Covalent Bonds
Polar covalent bonds occur when two atoms share electrons unequally due to differences in their electronegativities. This results in a molecule with a partial positive charge on one end and a partial negative charge on the other, creating a dipole. Water is a classic example of a molecule with polar covalent bonds, which contributes to its unique properties, such as high surface tension and solvent capabilities.
Recommended video: