Here are the essential concepts you must grasp in order to answer the question correctly.
Phage Conversion
Phage conversion refers to the process by which a bacterium acquires new traits through the integration of viral DNA from bacteriophages. This can lead to the expression of new phenotypic characteristics, such as increased virulence or antibiotic resistance, which can enhance the bacterium's survival and adaptability in various environments.
Recommended video:
Horizontal Gene Transfer
Horizontal gene transfer (HGT) is the movement of genetic material between organisms other than through traditional reproduction. In bacteria, HGT can occur via transformation, transduction, or conjugation, allowing for rapid acquisition of beneficial traits, such as those gained through phage conversion, which can confer competitive advantages in changing environments.
Recommended video:
Evolutionary Advantage
An evolutionary advantage refers to traits or characteristics that enhance an organism's ability to survive and reproduce in its environment. In the context of phage conversion, the new traits acquired can help bacteria evade host immune responses, resist antibiotics, or exploit new ecological niches, thereby increasing their fitness and likelihood of passing on these advantageous traits to future generations.
Recommended video:
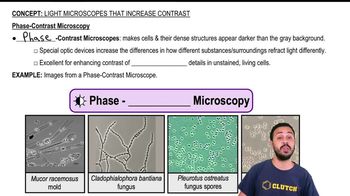
Phase-Contrast Microscopy
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance Verified Solution
Verified Solution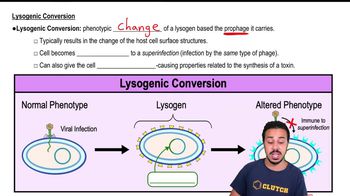


 3:52m
3:52m